ISO 11359-2:2021 Testing - Determination of Linear Thermal Expansion Coefficient and Glass Transition Temperature
This document specifies the method for testing using the thermal expansion method. It is used to determine the linear thermal expansion coefficient of plastics in the solid state by means of thermomechanical analysis (TMA). This document also specifies the method for determining the glass transition temperature using TMA. Note: The linear thermal expansion coefficient can be measured by various types of thermal expansion measuring instruments. This document only covers TMA instruments.
Differential Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion
The expansion quantity is normalized to the reference length Lo at room temperature. At temperature T and constant pressure p (expressed in reciprocal Kelvin), it is calculated according to the following formula:
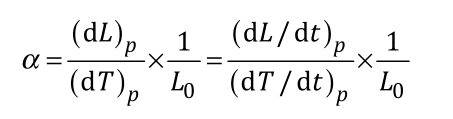
Where:
- Lo is the reference length at room temperature T0 along the measuring axis;
- L is the length along the measuring axis at temperature T.
For detailed test information, please refer to: Details of Thermal Expansion Coefficient Testing
Interpretation of ISO 11359-2:2021 Testing Service
The ISO 11359-2:2021 testing provided by Shanghai Jituo Material Technology focuses on the determination of the linear thermal expansion coefficient and glass transition temperature of plastics in the solid state. It adopts thermomechanical analysis (TMA) technology to provide key data support for the performance evaluation and application scenario adaptation of plastic materials.
1. Core Content of the Testing Standard
ISO 11359-2:2021 is a special testing standard formulated by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), with clear core definitions and scope of application:
- Testing Object: Only applicable to solid plastics, excluding liquid or molten plastics.
- Core Testing Items:
- Linear Thermal Expansion Coefficient (CTE): Reflects the expansion/contraction characteristics of plastics along the linear direction when the temperature changes, and it is a key parameter for evaluating the dimensional stability of materials.
