HotDisk
Testing is a technique used to measure the thermophysical properties of materials, such as thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity, and specific heat capacity. Its core principle is based on the transient solution of the heat conduction equation using the Transient Plane Source (TPS) method. Through specially designed sensors, it simultaneously achieves "heating" and "temperature monitoring", thereby quickly obtaining the thermophysical properties of the material.
Laser Flash Analyzer (LFA)
When a laser irradiates a material, the material is heated, generating a temperature gradient. When the temperature distribution inside the material reaches an equilibrium state, the laser pulse stops. By controlling the emission of the laser pulse and the temperature distribution within the material, the propagation time of the laser in the material can be observed with high accuracy. This time is used to calculate the thermal conductivity of the material.
Instrument and Parameters
- Instrument Model: Hot disk tps 2500s
- Technical Parameters:
-
- Thermal conductivity range: 0.005–500 W/m·K
-
- Temperature range: Room temperature (Hotdisk method
Sample Submission Requirements and Packaging
- Bulk Materials:
-
- Disc or rectangular shape with dimensions 30–50 mm.
-
- Metals: 8–12 mm thickness; ceramics: 5–10 mm; rubber/plastic: 3–6 mm.
-
- Surface must be smooth.
- Powders: More than 30 mL.
- Liquids: More than 30 mL.
- Samples must not decompose, explode, volatilize, or produce highly toxic gases within the testing temperature range, as this may cause irreversible damage to the instrument.
Testing Cases
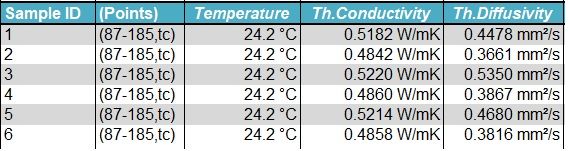
Reference Standards
- ISO 22007-2:2015 "Plastics - Determination of thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity - Part 2: Transient Plane Source (Hot Disk) method".
- GB/T 42919.1-2023 "Plastics - Determination of thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity - Part 1: General principles".

