Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
DSC is a thermal analysis technique developed from Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA). It is defined as a method for measuring the heat flow of a sample relative to a reference material under temperature program control, abbreviated as DSC (Differential Scanning Calorimetry). DSC technology facilitates quantitative data acquisition for thermal effects while retaining DTA functions. It is widely used to: Determine melting heat, crystallinity, and isothermal crystallization kinetic parameters of polymers;
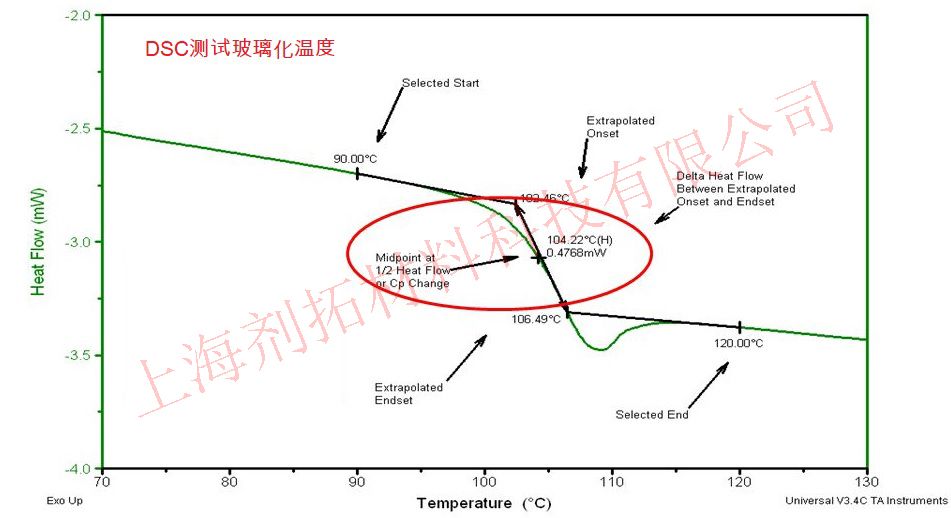
- Measure glass transition temperature (Tg);
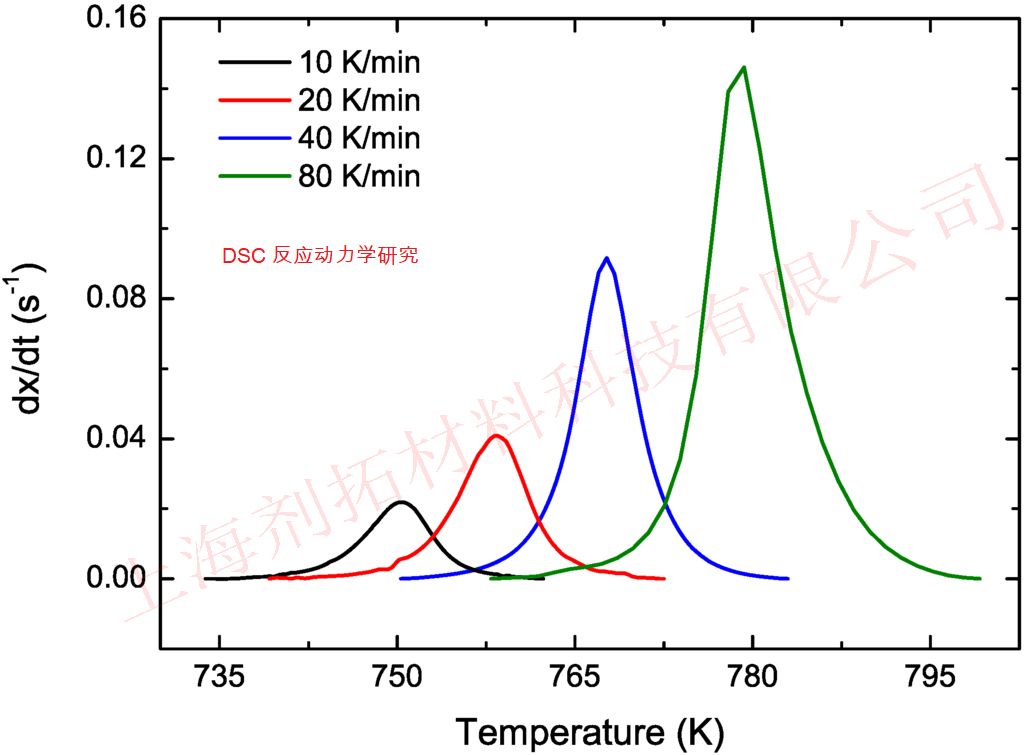
- Study reactions such as polymerization, curing, crosslinking, and decomposition;
- Determine reaction temperature/zone, reaction heat, and kinetic parameters.
Instrument Performance and Technical Parameters
- Model: TA Q2000
- Temperature Range: -75°C to 550°C (wide temperature coverage for multi-scenario thermal analysis)
- Temperature Accuracy: ±0.01°C (high-precision temperature control, data repeatability ≤±0.5%)
- Heating Rate: 0.1–100°C/min (supports conventional scanning and ultrafast kinetic research)
- Atmosphere Control: Nitrogen (N₂, 50 mL/min standard), customizable oxidizing atmosphere (advance application required)
Sample Requirements and Preparation Specifications
- Sample State Solid (powder/particles/film), liquid, gel
- Sample Amount 5–20 mg , <1 mg (micro-quantity)
- Drying Requirement Complete removal of solvents/moisture
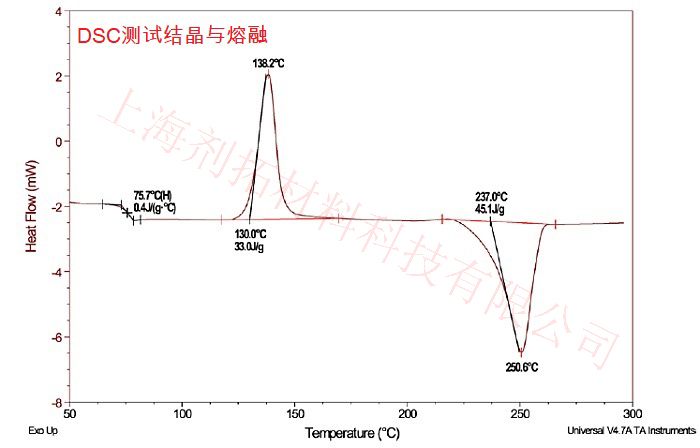
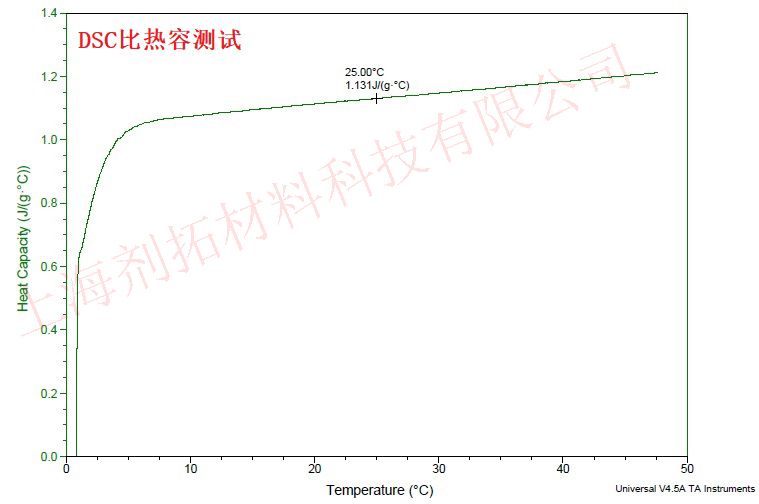
DSC Testing cases
Reference Standards and Hyphenated Technologies
| Testing Item | International/Industry Standards | Hyphenated Technology Expansion |
|---|---|---|
| Glass Transition Temperature | ASTM E1356, ISO 11357-2* | DSC-TGA Hyphenation (ASTM E1131) |
| Melting/Crystallization Behavior Analysis | ASTM D3418, ISO 11357-3* | EGA-IR Hyphenation (ISO 11358) |
| Oxidative Induction Time (OIT) | ASTM D3895, ISO 11357-6* | - |
| Specific Heat Capacity Measurement | ASTM E1269, ISO 11357-4* | - |
