Shanghai Jituo Hi-tech provides XRD performance testing and analysis services, which are applied to phase analysis (qualitative and quantitative) and characterization of material composition and phases.
XRD Principle
X-ray Diffraction (XRD) analysis is a structural analysis method that uses X-ray diffraction from crystals to study the spatial distribution of internal atoms in materials.
Instrument Model and Technical Parameters
- Instrument Model: BRUKER D8 ADVANCE
- Technical Parameters:
- Small-angle diffraction: Minimum angle 0.4°, mainly for mesoporous materials and polymer composites.
- Wide-angle diffraction: Minimum angle 5°, capable of accurately detecting diffraction peaks below 10°.
- Measurement accuracy: Angular reproducibility ±0.0001°; goniometer radius ≥200 mm, continuous adjustable diameter of the diffraction circle.
- Minimum step size: 0.0001°; angular range (2θ): -110° to 168°; temperature range: room temperature to 900°C.
- Maximum output: 3 kW; stability: ±0.01%; tube voltage: 20–60 kV (1 kV/step); tube current: 10–60 mA.
Sample Submission Requirements and Notes
- Solid powder: Uniform, dry, particle size <100 μm (passed through 80-mesh sieve), mass ≥100 mg.
- Bulk, metal, and film samples: Require a flat surface, approximately 20 mm × 10 mm × 2 mm.
Testing Examples
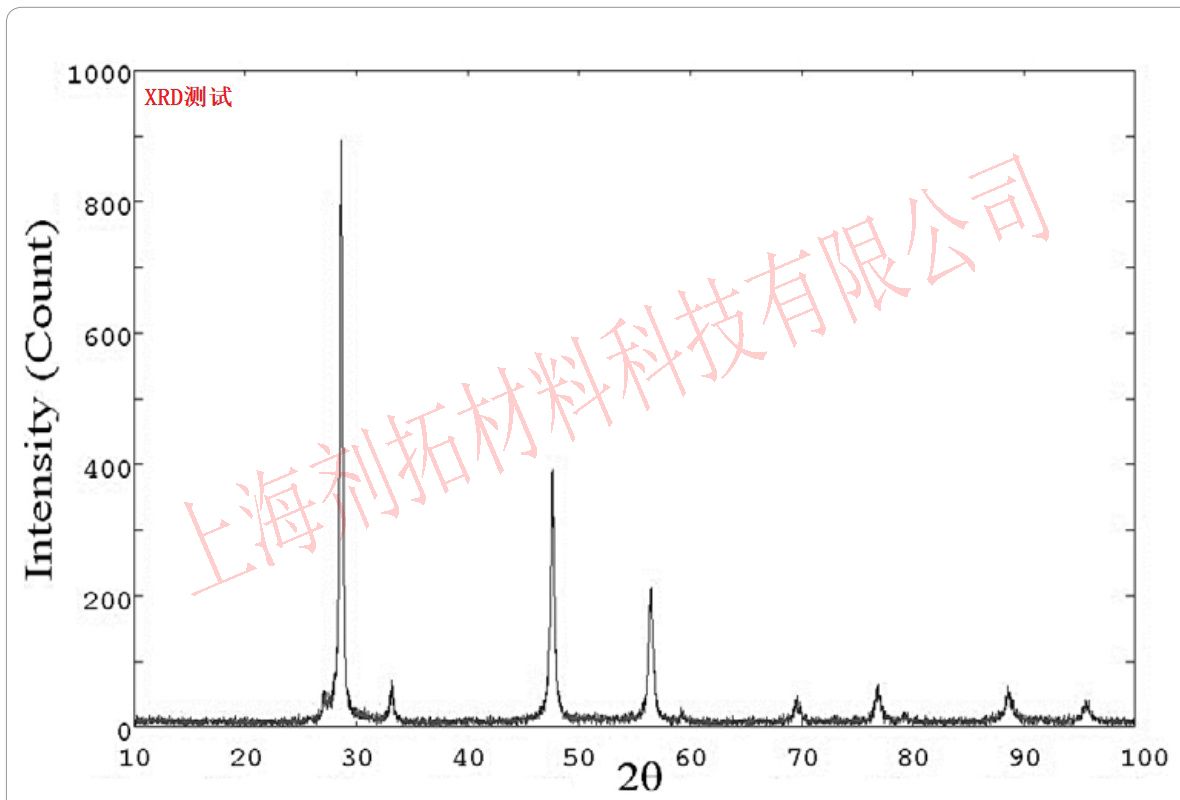
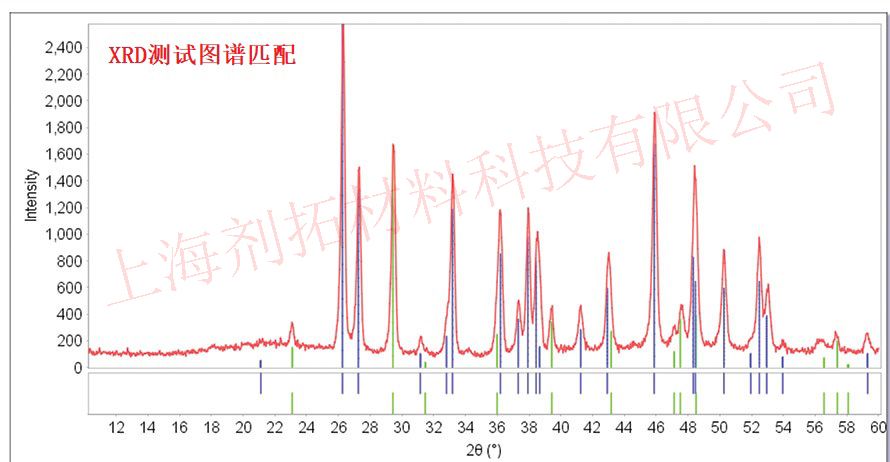
Reference Standards
- ISO 21068-4:2024 "Chemical analysis of raw materials and refractory products containing silicon carbide, silicon nitride, oxynitride and sialon—Part 4: XRD method"
- BS ISO 23071:2021 "Refractory products—Determination of reduced species in carbon-containing refractories by XRD method"
- GB/T 36655–2018 "Test method for α-crystalline silica content in spherical silica powder for electronic packaging—XRD method"
- GB/T 40407–2021 "X-ray diffraction analysis method for mineral phases of portland cement clinker"
- GB/T 36923–2018 "Pearl powder identification method—X-ray diffraction analysis"

