Principle of Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry (MIP)
Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry (MIP), also known as mercury porosity method, is a technique for measuring the pore size distribution of partial mesopores and macropores. The basic principle is that mercury does not wet ordinary solids, so external pressure must be applied to force mercury into pores. The greater the external pressure, the smaller the pore radius that mercury can enter. By measuring the amount of mercury intruding into pores under different external pressures, the pore volume corresponding to each pore size can be obtained.
Instrument Models and Parameters
- Instrument Model: Autopore IV 9500
- Technical Parameters:
- Maximum Pressure: 33,000 psi (228 MPa)
- Pore Size Measurement Range: 50 Å – 1000 μm
Sample Submission Requirements and Precautions
- Powder Samples: Volume ≥ 1 mL;
- Bulk Samples: Dimensions 0.2
1 × 0.21 × 0.2~1 cm; - Film Samples: Length 5~10 cm, Thickness ≤ 1 mm.
Testing Example
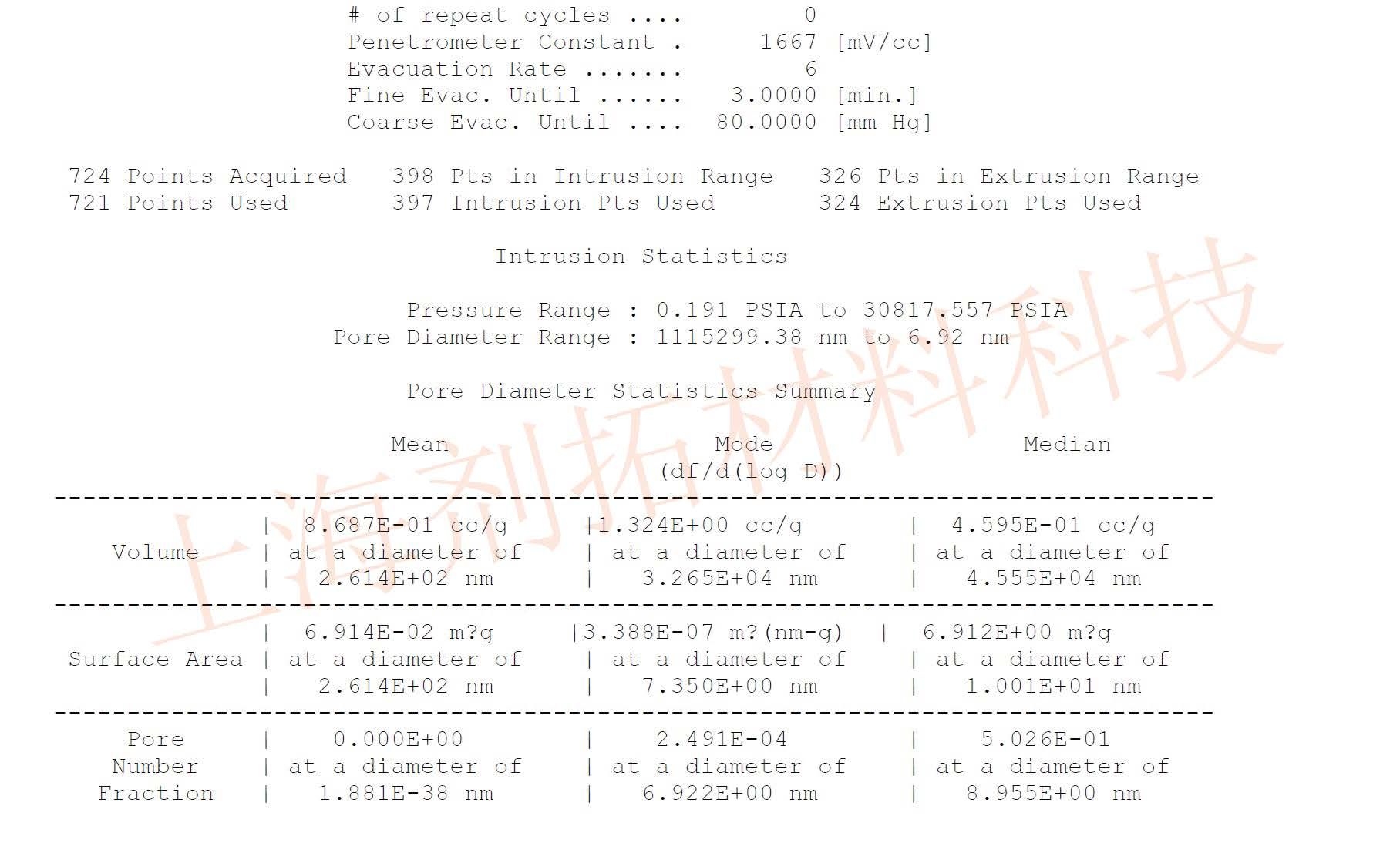
Reference Standards
- GB/T 21650.1-2008 Determination of Pore Size Distribution and Porosity of Solid Materials by Mercury Intrusion and Gas Adsorption – Part 1: Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry
- GB/T 50123-2019 Standard for Geotechnical Test Methods
- ISO 15901-1:2005 Solids – Porosity and Pore Size Distribution – Determination by Mercury Porosimetry and Gas Adsorption – Part 1: Mercury Porosimetry
- ASTM D4404-15 Standard Test Method for Determination of Pore Volume and Pore Volume Distribution of Soil and Rock by Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry
- ASTM D4641-10 Standard Test Method for Pore Volume and Area Distribution of Catalysts and Catalyst Carriers by Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry

